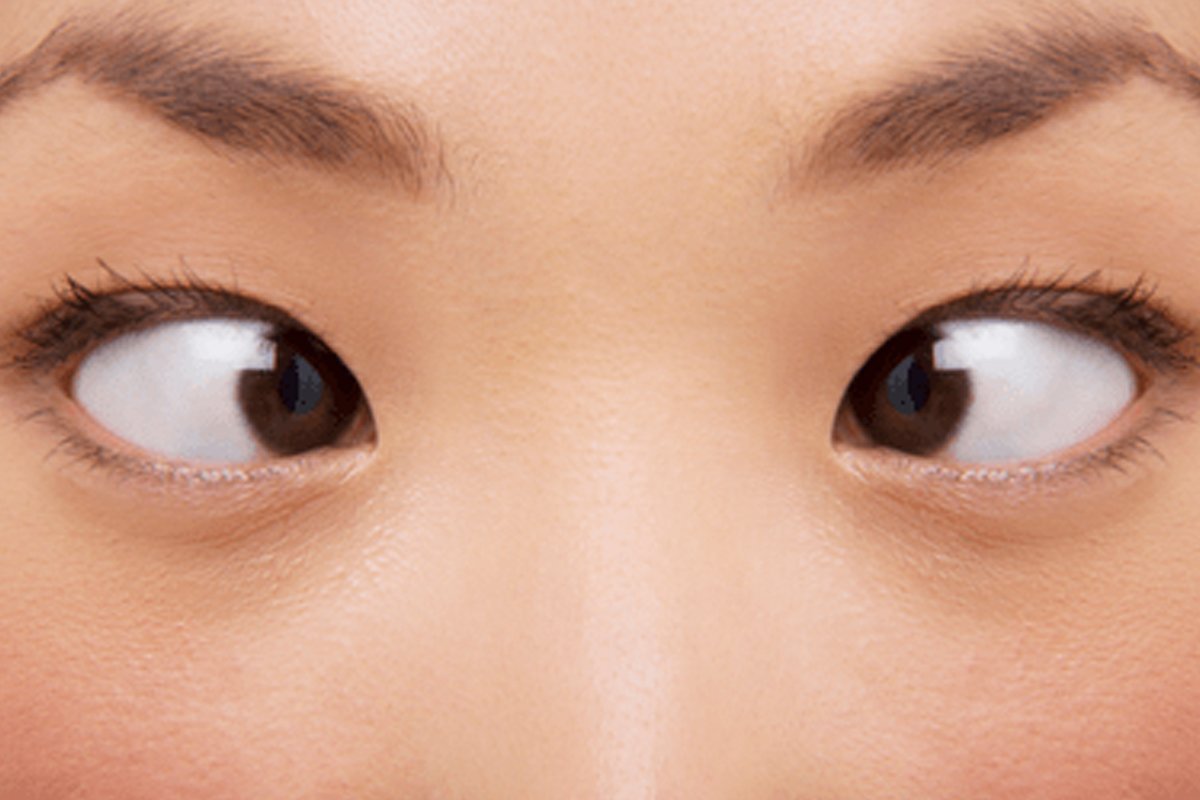
How do you examine a case of squint?
A squint, or strabismus, refers to a misalignment of the eyes that can lead to visual impairment and aesthetic concerns. Conducting a thorough examination is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
The process begins with a meticulous examination of your visual acuity to determine the sharpness and clarity of your vision. Computerized refractive testing is employed to assess any refractive errors, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism, ensuring accurate prescription for corrective lenses if needed.
Clinical History
Gather detailed information about the patient's medical and ocular history, including the onset of squint, family history, and any associated symptoms such as double vision or headaches.
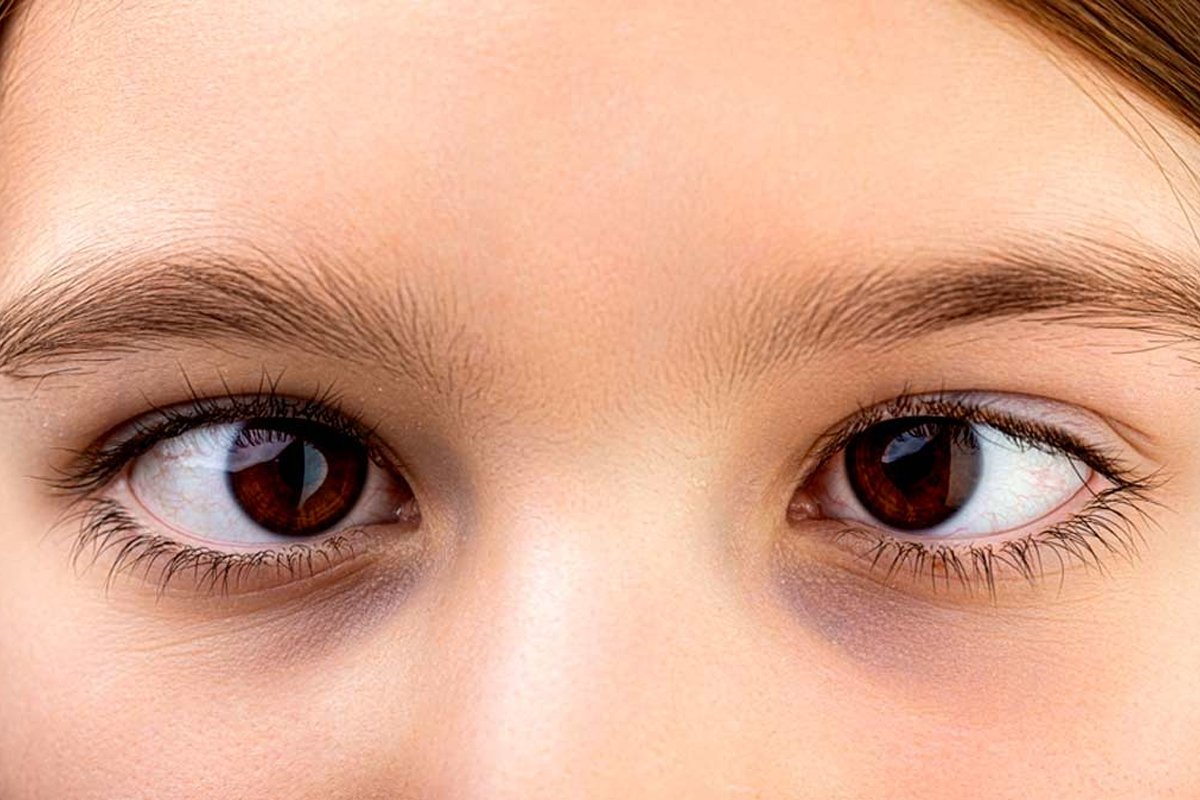

Visual Acuity Assessment
Perform a comprehensive visual acuity test to evaluate the clarity of vision in each eye individually and assess the potential impact of squint on visual function.
Ocular Motility Examination
Evaluate the range of eye movements to identify
limitations or abnormalities in eye coordination. Assess the six cardinal positions of gaze to pinpoint specific muscles involved.
Conduct the cover-uncover test to detect latent squint, where one eye may deviate when the other is covered, revealing hidden misalignments.
Stereopsis and Binocular Vision Testing:
Assess stereopsis and binocular vision to determine the degree of eye coordination and depth perception impairment, providing insights into the functional impact of squint.
Refraction Test:
Determine the refractive error in each eye to address any underlying vision issues contributing to squint and prescribe corrective lenses if necessary.
Fundus Examination:
Examine the fundus to rule out any structural abnormalities, such as retinal diseases, that may be associated with or contributing to squint.
Orthoptic Assessment:
Engage in orthoptic assessments, including prism cover tests, to measure the deviation angle and guide the selection of appropriate therapeutic interventions.
